An intelligent AI-powered chatbot that transforms natural language requests into structured, location-based educational tasks for interactive event experiences. Built with GPT-4o, Firebase Realtime Database, Node.js, and Flutter.

Deckle is an event platform that enables organisers to create interactive, gamified experiences—think scavenger hunts, trivia challenges, and team-building activities. However, the existing task creation workflow was entirely manual. Event organisers had to painstakingly craft each task individually: writing questions, setting locations, choosing task types (photo challenges, multiple choice, drawing prompts), and configuring point values. For an event with 20+ tasks, this process could take hours.
The bigger challenge was accessibility. Not every event organiser is a game designer. Many users struggled to come up with creative, engaging tasks that matched their event's theme, location, and audience. They needed inspiration, but the platform offered none. The result? Events that felt generic, tasks that lacked cohesion, and organisers who abandoned the platform before launching their first experience.
We needed a solution that could understand what an organiser wanted—even when they couldn't articulate it perfectly—and generate professional-quality tasks in seconds rather than hours.
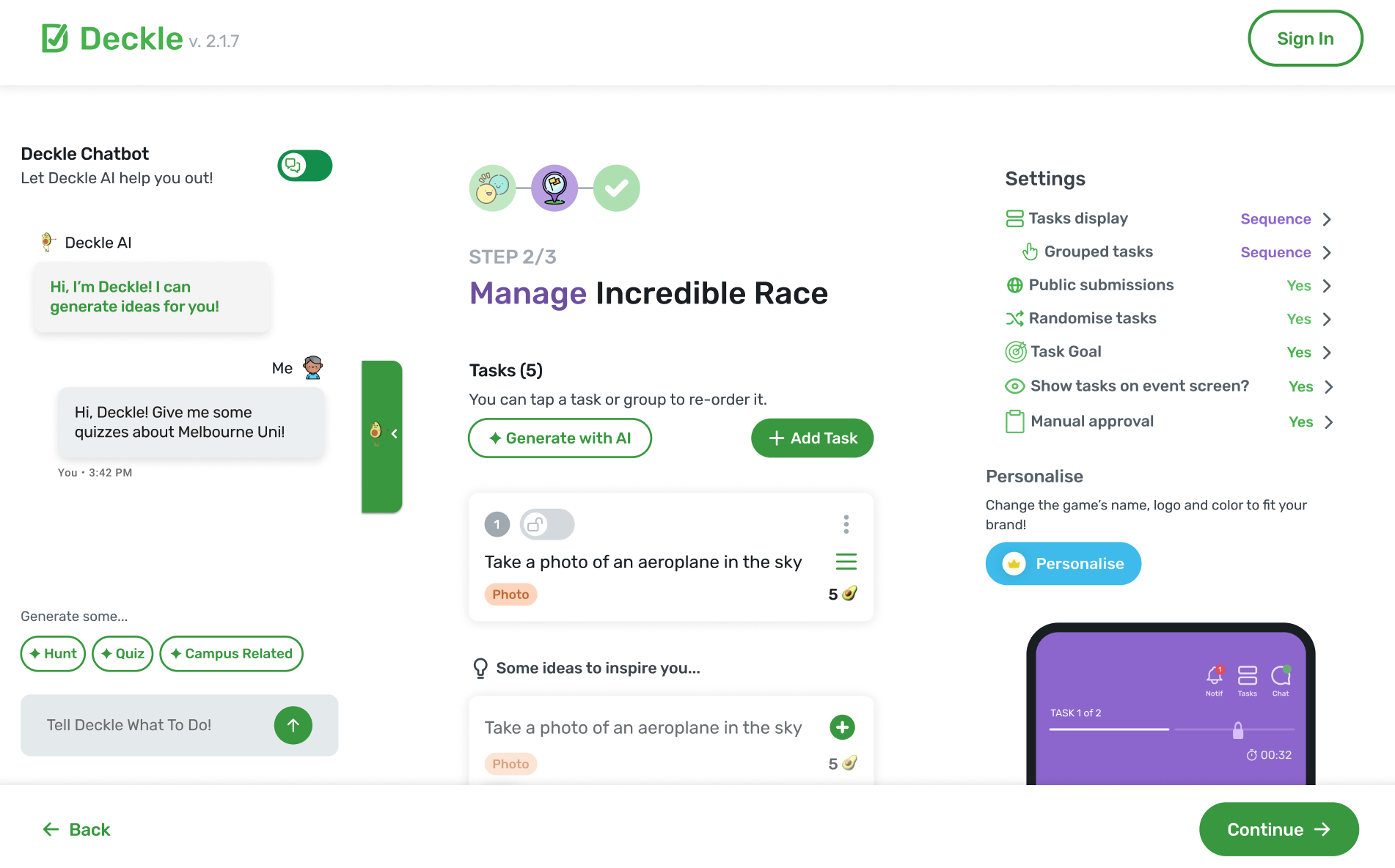
I designed and built an AI-powered chatbot assistant that acts as a creative partner for event organisers. Users can simply describe their event in natural language—"I'm planning a history-themed scavenger hunt around Melbourne for university students"—and the system generates a complete set of structured, themed tasks tailored to their requirements.

The solution consists of three interconnected layers: a conversational Flutter interface where users interact with the AI, a Node.js/Express backend that orchestrates the AI pipeline and manages business logic, and Firebase Realtime Database that persists conversation context and enables real-time synchronization across devices. At the heart of it all is a sophisticated prompt engineering system that transforms vague requests into precisely structured educational tasks.
What makes this chatbot unique is its context awareness. Unlike simple one-shot generators, Deckle's AI remembers the conversation. It extracts keywords from previous interactions, generates rolling summaries, and uses this accumulated understanding to produce increasingly relevant suggestions. Ask for "something harder" or "more creative tasks," and it understands exactly what you mean based on what came before.
The chatbot automatically distinguishes between three types of user input: task generation requests ("create a quiz about Australian wildlife"), general questions about the system ("how many tasks can I create?"), and conversational chat ("thanks, that looks great!"). This is achieved through a confidence-scored classification system—inputs must exceed a 0.6 confidence threshold before the system commits to an interpretation, reducing misclassification errors and improving user trust.
Users speak naturally; the system thinks in structured parameters. A request like "outdoor team activity at RMIT, about 45 minutes, medium difficulty, focused on Melbourne history" is parsed into 13 distinct fields: location, venue type, indoor/outdoor preference, team format, duration, difficulty level, theme, topic, and preferred task types. This parsing happens through a carefully engineered GPT-4o prompt that defaults intelligently when information is missing—if you don't specify difficulty, it assumes "Medium"; if you mention "university," it infers "Indoor."
The system generates six distinct task types: multiple choice questions with validated answer options, photo challenges with GPS coordinates, video recording prompts, creative drawing tasks, text-based trivia with expected answers, and QR code scavenger hunts. Each task type has specific validation rules—MCQs require 3-5 choices with a marked correct answer; location-based tasks include latitude/longitude coordinates; drawing prompts are filtered to ensure they're achievable in under 2 minutes.
Every interaction builds on the last. The system extracts keywords from user requests and generated tasks, then uses GPT-4o to generate professional conversation summaries that capture the progression of the dialogue. This context is persisted to Firebase and loaded on subsequent requests, enabling natural follow-ups: "make those easier," "add more photo tasks," or "switch to a science theme." The AI understands these relative references because it remembers what "those" refers to.
Generated tasks aren't just displayed as text—they're rendered as interactive cards directly in the chat interface. Each card shows the task type with a visual indicator, the challenge prompt, point values, and for location-based tasks, a preview of where on the map the activity takes place. Users can review, edit, or regenerate individual tasks without losing the rest of their set.
This project transformed my understanding of NoSQL database design. Firebase's hierarchical JSON structure initially felt limiting coming from relational databases, but I learned to embrace denormalization as a feature rather than a compromise. Rather than joining tables, I structured data paths like /chatBotEventMessages/{eventId}/{chatId}/{messageId} to enable instant queries without complex lookups.
The real revelation was real-time synchronization. Using Firebase's onValue listeners on the Flutter client and admin.database().ref().set() on the server, I built a system where messages appear instantly across devices without polling. When the AI generates tasks, they're written to Firebase and immediately reflected in every connected client. I learned to think about data not as static records but as living streams.
I also gained practical experience with Firebase Admin SDK patterns: using .push() for auto-generated keys, .update() for partial modifications, and .once('value') versus continuous listeners. Managing 276+ database operations across 20 controllers taught me the importance of consistent error handling—every database call is wrapped in try-catch blocks with meaningful error logging, because silent failures in async operations are debugging nightmares.
Building the chatbot backend solidified my understanding of RESTful API architecture. I structured the codebase with clear separation of concerns: routes handle HTTP semantics and request parsing, controllers contain business logic and orchestration, models define validation schemas, and services abstract external integrations. This modularity meant I could swap OpenAI for a different LLM provider by changing a single service file.
I implemented middleware chains for the first time in a production context. Every request passes through authentication middleware that validates JWT tokens, then through Joi schema validation that catches malformed requests before they reach business logic. This layered approach caught countless bugs early and made the API self-documenting—the schema files serve as living documentation of what each endpoint expects.
Error handling at scale was a major learning area. I built a consistent error response format with fallback messages, ensuring that even when OpenAI's API fails (rate limits, timeouts, malformed responses), users receive graceful degradation rather than cryptic 500 errors. The fallback system uses pre-defined sample tasks and hardcoded suggestions when AI generation fails, maintaining a functional (if less magical) experience.
Working with Firebase Cloud Functions taught me the serverless paradigm's tradeoffs. Cold starts were initially a pain point—the first request after idle time took 3-4 seconds. I learned to optimize by minimizing top-level imports, lazy-loading heavy dependencies, and keeping the function bundle lean. The emulator workflow (firebase emulators:start --import=./mockserver) became essential for rapid iteration without burning through API quotas.
This project was my deep dive into the art and science of prompt engineering, and it fundamentally changed how I think about AI integration. I learned that prompts aren't just instructions—they're programs written in natural language, with their own debugging challenges and optimization strategies.
My first major lesson was the importance of structured output. Early prompts produced beautifully creative tasks that were impossible to parse. By specifying "response_format": {"type": "json_object"} and including explicit schema examples in the system prompt, I achieved 99%+ parse success rates. I also built a cleanJsonResponse() function that strips markdown code fences and handles edge cases where the model wraps JSON in explanation text.
Temperature tuning was more nuanced than I expected. For conversation summaries, I use 0.5—low enough for factual consistency but not so low that summaries feel robotic. For task generation, I push to 0.9 for maximum creativity. For intent classification, I keep it at 0.7 to balance reliability with flexibility. Each use case demanded its own calibration.
Context window management became critical as conversations grew. Rather than stuffing entire conversation histories into prompts (which quickly exceeded token limits), I implemented a summarization layer. After each interaction, GPT-4o generates a 150-token summary that captures key information—themes, preferences, generated task types—which is then fed into subsequent requests. This "memory compression" technique keeps context relevant without ballooning costs.
I learned to write defensive prompts. The task generation prompt explicitly states what NOT to do: "Avoid interviews, opinions, personal experience, or complex multi-step setup. Avoid vague reward phrases like 'to unlock a surprise.' Avoid generic QR code task titles like 'Hidden Message' or 'Secret Code.'" These negative instructions were added iteratively as I encountered failure modes in production. Prompt engineering is as much about preventing bad outputs as enabling good ones.
Perhaps the most valuable lesson was treating prompts as code. I version-controlled them, A/B tested variations, and built constants files (CHATBOT_VALID_TASK_TYPES, CHATBOT_MCQ_CHOICES) to ensure consistency. When a prompt change broke task validation, I could roll back just like reverting a bad commit.
Designing a chat interface taught me that conversational UI is deceptively complex. It's not just a list of messages—it's a dynamic, stateful, real-time experience that must feel responsive even when the backend takes seconds to respond.
The loading state problem was my first challenge. AI responses take 2-5 seconds, an eternity in UI terms. I implemented a "typing indicator" pattern: immediately display a bot message with a shimmer animation, then replace it with actual content when the response arrives. This preserved conversational flow and set user expectations without blocking interaction.
I built a component architecture that could render diverse content types in a unified chat stream. The ChatMessageComponent handles plain text, loading states, multi-choice options, and rich task cards—all within the same message bubble paradigm. This required careful conditional rendering and a flexible data model that could represent any message type.
Auto-scrolling seemed trivial but had surprising edge cases. Scroll-to-bottom on new messages is essential, but it must not interrupt if the user has scrolled up to review history. I implemented scroll position detection to only auto-scroll when the user is already at the bottom, preserving their review context otherwise.
The suggestion chips feature ("Generate some... 🎯 Trivia | 📸 Photo Hunt | 🎨 Creative") taught me about reducing input friction. By offering contextual one-tap actions, users could iterate quickly without typing. These chips are dynamically generated based on conversation state and previous task types, making the interface feel intelligent and anticipatory.
Color and typography decisions had UX implications I hadn't anticipated. Bot messages use a lighter background (gray10) while user messages use slightly darker (gray20)—this subtle difference creates clear visual separation without harsh contrasts. Message bubbles have max-width constraints (350px) to prevent wide messages from feeling overwhelming on large screens while ensuring readability on mobile.
Early task generation produced content that felt generically AI-written—vague prompts, overused phrases like "explore and discover," tasks that could apply to any location. I combated this through aggressive negative prompting (explicitly banning common AI-isms), by requiring location-specific details in every task, and by implementing a validation layer that rejects tasks missing concrete details. The system now produces tasks that feel hand-crafted.
After 10+ exchanges, the AI would "forget" early context, generating tasks that contradicted earlier preferences. The solution was the summarization pipeline—instead of passing raw history, I generate compressed summaries that capture intent rather than verbatim text. This gave the AI a stable "memory" without token bloat.
GPT-4o occasionally returns JSON wrapped in markdown, incomplete arrays, or responses that technically parse but fail validation (e.g., MCQ with only 2 choices). I built a multi-stage cleaning and validation pipeline: strip markdown, attempt JSON parse, validate against schema, fix common issues automatically (add missing fields with defaults), and only then surface to users. This defensive approach means users almost never see raw errors.
When the AI writes a message to Firebase while the client is simultaneously sending a new request, ordering gets confused. I solved this with timestamp-based ordering at the database level and optimistic UI updates on the client—display the user's message immediately while the server catches up. Firebase's atomic operations ensured consistency even under concurrent writes.
The chatbot reduced average task creation time from 45+ minutes of manual work to under 2 minutes of conversational interaction. User testing showed that first-time organisers could generate a complete, themed event in a single session—something that previously required tutorials and multiple attempts.
More importantly, the quality of generated content exceeded what most users could create manually. The AI's knowledge of historical facts, creative challenge types, and location-based engagement patterns meant that even non-designers could produce professional-quality experiences.
Building Deckle's AI chatbot taught me that the magic of modern AI products isn't in the model—it's in the orchestration. GPT-4o is powerful, but it's the prompt engineering, context management, validation layers, error handling, and thoughtful UX that transform raw capability into a product people love using.
I emerged from this project with production-grade skills in full-stack AI development: from Firebase schema design to Express middleware to prompt iteration to Flutter state management. More than any single technology, I learned to think systemically—how each layer must anticipate and handle failures from adjacent layers, how user experience depends on invisible backend reliability, and how AI augmentation works best when it feels like collaboration rather than automation.
The Deckle chatbot represents my most complete work to date: a system where database, backend, AI, and frontend come together as a cohesive product that genuinely makes users' lives easier.